
Recent Cyberattacks Increasingly Target Tier 1 Companies/Individuals
SYNOPSIS:
This months blog is a multi-part writing consisting of two completely different topics; first we wrap up the cyber-security series noting the GoDaddy hack. Several of our customers were affected by this hack and 2 customers lost 50% of their revenue for 3 weeks. That revenue was syphoned to off-shore accounts that US laws have no jurisdiction over. Next, we begin our educational series covering the most all of the common Apple and Microsoft systems and applications in use today. Hopefully, all readers will gain substantial knowledge. We welcome your feedback and suggestions for additional content.
1] Protect Data, Devices, and Identities with These 5 Tips
Over the last few weeks, cyberattacks have impacted individuals and businesses around the world. A new technique called HTML smuggling allows hackers to embed malicious scripts inside innocuous-seeming emails. A recent attack on web hosting giant GoDaddy exposed the email addresses of 1.2 million customers most of whom manage WordPress accounts. Microsoft had to issue emergency patches to fix active flaws in its heavily used Excel and Exchange applications. And HP revealed critical vulnerabilities in several consumer printer models.
Even an escalating cyberwar between Israel and Iran is now targeting ordinary civilians. In November, Irans 4,300 gas stations were paralyzed for 12 days. Two weeks later, a retaliatory attack exposed the hospital records and dating app details of 1.5 million Israelis or 15 percent of the country’s total population. Those intrusions then cascaded, compromising Instagram, Facebook, and Gmail accounts of those affected.
These represent some of the most prominent instances of civilians being targeted by a significant cyberattack. Security experts worry it could become a disturbing new trend once hackers realize how much chaos and suffering such attacks may cause.
How can you protect your business—and the individuals that make up your workforce?
It’s no longer feasible to wait for a cybersecurity problem before taking action to secure your data, your devices, and the digital identities of your staff members. In today’s increasingly interconnected world, it’s not so much a matter of if you will be hacked but rather when and how bad the attack will be. As hackers develop more complex tactics, companies and their employees must have contingency plans in place to secure networks, protect devices, and maintain day-to-day operations.
At J&S Systems Division, we have gathered five important steps you can take to mitigate the threat you might face from increasing cyberattacks, data breaches, and other online problems.
1) Extend cybersecurity protection to every device used by your employees.
As more and more companies have shifted toward hybrid and remote work, millions of individuals across North America have started using unprotected laptops, tablets, smartphones, and Wi-Fi routers. If they haven’t already, these devices need to be brought inside your company’s ring of protection immediately. It’s important to extend these extra layers of IT security using remote desktop protocols, cloud-based app management, enhanced network protection, and even multi-factor authentication for safer user access.
2) Assess any desktops or laptops for out-of-date operating systems.
What many business owners consider a nuisance can in fact be a serious security problem. Last year, millions of machines powered by Windows 7 reached their end of life after Microsoft discontinued support for the legacy operating system. In 2017, the ransomware infection WannaCry targeted computers still running Windows XP after that end of support, exploiting a known vulnerability to steal unsecured data and shut down millions of interconnected systems. Instead of waiting for your systems to reach this end of support point, assessing them now will help you develop a smart plan for upgrade or replacement moving forward.
3) Make sure all company data is backed up safely and securely.
If you’re not backing up your information regularly, remotely, and redundantly, your business is probably at risk. Most ransomware attacks have such a devastating effect precisely because companies don’t have access to backup copies of recent data. That leaves them no choice but to give in to a hackers demands and pay thousands of dollars of ransom to try and retrieve stolen or encrypted information. Investment in this area pays off, too, protecting against everything from natural disasters to user error to hardware failure. All it takes is a couple of days of significant data downtime to severely affect your company’s bottom line, where a reliable data backup and recovery protocol could have you back up and running in hours instead of weeks.
4) Give your employees regular cybersecurity training and ongoing education.
Many data breaches and cyberattacks are caused by seemingly simple behaviors: clicking on a web link in an email, downloading an infected attachment, or divulging private information to a bad actor posing as a colleague or boss. That’s why employee training is so important. Savvy employees who know how to spot cyberattacks in the wild can serve as a critical first line of defense, flagging spam emails or alerting IT professionals to suspicious online activity that can then be addressed by trained technicians.
5) Work with an IT support team that understands your company.
A part-time employee handling computer issues on the side won’t get it done. In our rapidly changing online world, your business deserves dedicated IT support that addresses short-term vulnerabilities while working with you to develop a long-term strategy for business success. A proactive approach can mitigate many of the risks outlined above it doesn’t matter if you’re a large enterprise with multiple locations and hundreds of employees scattered around North America, or a small neighborhood business with just a few individual staff members.
At J&S Systems Division, our goal is to keep every employee and every device safe. With more than 200 offices and 800 technicians spread across North America, we serve as a trusted business partner to thousands of clients, working 24/7/365 to defend your data, strengthen your systems, and empower your employees to work smarter and more efficiently.
Want to grow your business instead of worrying about a cyberattack? Looking to beef up cybersecurity while avoiding a data breach? Contact J&S Systems Division today.
2] Microsoft Excel Workbooks and Worksheets: What’s the Difference?
Knowing Excel is a valuable skill. But the tool is not always easy to use and can be frustrating if you don’t fully understand the features. That’s often the case with Excel worksheets vs. workbooks because they are terms that you can easily confuse. In fact, this confusion leads to some people referring to worksheets as spreadsheets. Workbooks and worksheets are created and managed differently, so it’s essential to know the difference between them.
In this Excel tutorial, you’ll learn what is the difference between a worksheet and a workbook. You will also learn how to manipulate worksheets and move them from one workbook to another. Also, if you want to become a power user, make sure to check out our 40 best Excel keyboard shortcuts and macros to speed up your workflow.
What’s the Difference Between Worksheets and Workbooks?
Imagine a workbook as a regular paper book; it’s a collection of pages. An Excel worksheet is just a single page, or one sheet of the many pages that are in the book. That means that an Excel workbook is a collection of worksheets but it can also contain a single worksheet. How many worksheets can you put in one workbook? Microsoft says that it depends on your computers hardware. You can have any number of worksheets in a workbook, as long as your device allows it.
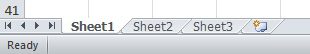
When you first open Excel, the software will present you with a workbook with three empty Excel sheets. You can see them in the bottom left corner of the screen as separate tabs named Sheet1, Sheet2, and Sheet3. You may need to use just one of these three, but you don’t need to delete the ones you are not using.
Excel worksheets are made of rows, columns, and cells in which you can input data such as dates, text, numbers, and Excel formulas and functions. The data you enter in the worksheet cells, rows, and columns can also be displayed in graphs and charts.
You can save Excel workbooks on your device with the file extension xlsx. However, the older version of the software used the xls extension so don’t be surprised if you see this instead of xlsx. Don’t worry, any new version of Excel can open both types of file extensions.
Grouping worksheets in a workbook is handy. You would want to keep worksheets that contain closely related data in one place. Workbooks are convenient if you are linking data from one worksheet to another. Workbooks are just like folders that keep different but related files together. However, hopping from one worksheet to another can be very confusing, and this is why you should learn how to manage them properly.
How to View, Rename, Insert, and Delete a Worksheet
The default names Excel gives to worksheets are not very descriptive. There is not much information in Sheet1, Sheet2, and Sheet3. So, you should first learn the basics about worksheets.
Viewing Worksheets
All you have to do to view a single spreadsheet is to click on its tab. But if you are working with many sheets with longer names, Excel won’t be able to display all the sheet tabs. In that case, you can use the arrows to the left of the tabs. These arrows will help you navigate left or right. You can also right-click on said arrows and a list of all the tabs will be displayed. Then you can just click on the desired worksheet.
Renaming a Worksheet
Renaming a worksheet is easy. Just right-click on the tab and a context menu will open. Choose Rename and type in the new name. You can also double-click the tab you want to rename and type the new name.
Inserting a New Worksheet
Did you notice a small tab with a file icon next to the worksheet tabs? Click on it and a new worksheet will appear to the right of the last one. This is the fastest and easiest way to open a new worksheet. Another way to insert a new worksheet is to select the tab to the right of where you want to insert a new one, then right-click and select Insert.
A new pop-up window will open. Select the worksheet and click OK.
Deleting a Worksheet
Deleting worksheets is simple. Right-click on the tab of the worksheet. A context menu will appear and simply click Delete.
In your Inbox Next Month¦
Excel Primary finish up Microsoft Sway vs. PowerPoint: What’s Similar and What’s Different?
